Concrete Driveway Thickness: Meet the Standards

Last updated on May 14th, 2022
Concrete driveways are generally considered as non-structural members. They usually do not transfer loads or stresses from other elements of the structure to the ground. Hence, their problems do not affect the structural integrity of the building.
Nevertheless, the thickness of a concrete driveway is an essential parameter that can affect its overall performance. For this reason, codes, standards, guidelines, and datasheets that cover concrete driveways usually specify minimum thickness requirements. Also, all design methods for slabs on ground do consider thickness as a major parameter in their calculations. In fact, concrete driveway thickness can be influenced by various factors.
The 3 main factors that affect the thickness of concrete driveways
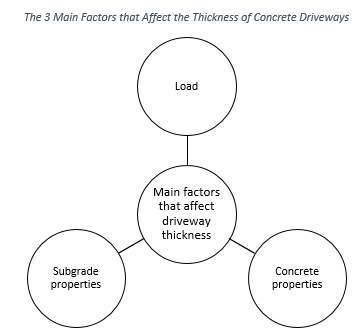
The three key factors that affect concrete driveway thickness include load, concrete properties, and subgrade properties.
Load
The magnitude of the load, its contact area, location, and the spacing between the loads have a large influence on the thickness requirements. For example, having a heavy truck’s load on the driveway is much different than having a relatively light-weight vehicle’s load.
Concrete properties
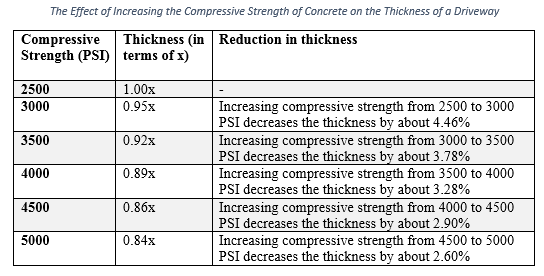
The properties of concrete have a major effect on the thickness requirements of a concrete driveway. These mainly include the compressive strength, flexural strength, elastic modulus, Poisson’s ratio, and stiffness. Mainly, when applying a load to the driveway, concrete exhibits stresses and transfers the load to the underlying support. But for the concrete to withstand these stresses, it should have a higher bearing capacity. For example, the tensile strength of concrete should be higher than the tensile stresses, else it will crack.
The following table shows an estimate of the effect of the compressive strength of concrete on the thickness of the driveway.
Subgrade properties
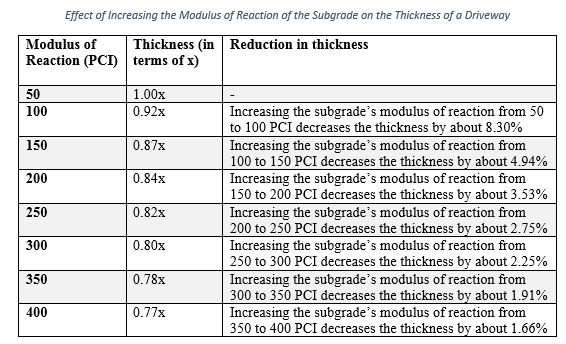
Also, the subgrade properties influence the thickness requirements, but not significantly. These properties mainly include the modulus of reaction and the stiffness. In fact, the concrete driveway transfers the load to the base and the sub-grade, which should be able to effectively resist the stresses. For instance, the subgrade should not excessively deform under the application of the load. Else, the slab would not be able to transfer the load effectively to the underlying support, and would eventually fail.
The following table shows an estimate of the effect of the subgrade’s modulus of reaction on the thickness of a concrete driveway.
What to consider when determining the concrete driveway thickness
Based on the previous section, the thickness mainly depends on the load, concrete properties, and subgrade properties.
In addition, there are building codes, data sheets, regulations, and codes of ordinances that specify the minimum thickness requirements for concrete driveways. These requirements may vary depending on the location, and are sometimes specified based on the loads of the vehicles in service. For example, the minimum concrete driveway thickness may vary between one country and another, between states, and between cities.
Determining the required concrete driveway thickness
The thickness of concrete driveways is usually determined according to the requirements of local regulations only, or according to an engineering structural design which still meets the requirements of local regulations. In fact, the suitable method depends on the type of the driveway, loads, and on the regulations.
Determining the concrete driveway thickness according to local regulations
In this method, the required thickness of a concrete driveway is determined solely according to the contractor and to the requirements of local codes without detailed structural calculations by an engineer.
This method is usually suitable for basic non-structural residential concrete driveways subjected to the loads of common residential vehicles and pedestrians, and where there are no obligations for a detailed structural design by local codes.
Why? Because basically, concrete driveways are non-structural members, unless they transfer loads from other structural elements of the building to the ground. Thereby, if such driveways (non-structural) suffer from problems, such as cracks, they would not affect the structural integrity of the building.
Also, the common vehicles in service for residential concrete driveways are residential vehicles of normal weight such as cars and basic SUVs.
In addition, the minimum thickness requirements in local codes are usually set considering various local factors and the load of the common vehicles in service. Nonetheless, some local data-sheets, such as the CCAA, specify minimum driveway thicknesses for different ranges of vehicles’ weights up to 10 metric tons.
For these reasons, basic non-structural residential driveways are often installed with a thickness according to the requirements of local codes without detailed calculations by an engineer.
Commonly, the contractor asks the client a few questions to know about the loading conditions, exposure conditions, and other useful information. Then the contractor decides how thick the concrete driveway should be based on their experience and awareness of the local regulations. Mainly, the thickness should be at least equals to the minimum requirements set by the regulations.
Determining the thickness of a concrete driveway according to engineering designs
The other method basically involves the expertise of an engineer. Where, the engineer determines the thickness based on engineering design methods, while still conforming to local codes.
This method is usually used in structural concrete driveways or parking pads. For example, a driveway, or part of it, that is structural, meaning that it transfers loads (horizontal or vertical) from other structural elements of the building to the ground.
Also, this method is used in special driveways, or when required by the regulations. For example, the CCAA datasheet states that concrete driveways that are used by heavy vehicles, exceeding 10 metric tons, require an engineering design.
“Pavements for heavier vehicles than this will require more detailed design by a qualified engineer.” ~ CCAA -2017- Residential Driveways and Paths.
In addition, ACI 332-14 chapter 10 commentary R10.1 states that if the supporting subgrade is not suitable to carry the loads, or if the slab is not continuously supported or if it is placed over voids, then it should be designed and constructed as a structural slab.
“Any slab placed on soil not suitable to support the imposed loads, located over voids, or otherwise not continuously supported should be designed and constructed as a structural slab.” ~ ACI 332-14.
Meet the concrete driveway thickness standards
Meeting the thickness standards means that when constructing a driveway, it is important to have its thickness at least equals to the minimum requirements set by the local regulations.
Examples of determining the thickness of concrete driveways
In the following section, we will give two examples on how to determine the thickness requirements of a concrete driveway. We will consider one example in Australia, and another in the United States.
Example 1: Australia
In this example, we will consider three residential driveways, A, B, and C, in Brisbane City in Australia. Driveway A has residential vehicles in service, where the gross mass of a vehicle ranges between 1.5 and 2.6 tonnes. Whereas, driveways B and C will have trailers frequently parked on with 8 tonne and 14 tonne gross mass, respectively. Regardless of all other conditions, or the legality of parking such vehicles on residential driveways, how thick should each driveway be?
For this example, we will determine the thickness by referring first to the Brisbane City Council – Driveway Technical Standards, and to the Cement Concrete and Aggregates Australia (CCAA) datasheet – Residential Concrete Driveways and Paths.
Driveway A: Based on the Brisbane City Council – Driveway Technical Standards, the driveway must have a minimum thickness of 125mm. However, we will also take a further step forward to consider the CCAA datasheet. According to the CCAA, the driveway should have a minimum thickness of 100mm for vehicles of less than 3 tonne gross mass.
Hence briefly, driveway A should ideally have a minimum thickness of 125mm.
Driveway B: According to the Brisbane City Council – Driveway Technical Standards, the driveway should be at least 125mm thick. But, according to the CCAA datasheet, the driveway should have a minimum thickness of 150mm for vehicles of gross mass between 3 and 10 tonnes.
Thereby, driveway B should ideally have a thickness of more than 150mm.
Driveway C: As already mentioned previously, the city’s technical standards for driveways states that the minimum thickness should be 125mm. However, considering the CCAA datasheet, the driveway requires a detailed design by an engineer, since the frequent vehicle in service has a gross mass exceeding 10 tonnes.
Thus, driveway C ideally requires a detailed engineering design.
Example 2: United States
In this example, we will simply show the differences in the thickness requirements between different cities in different states. Let us consider the following four cities:
- City of Boca Raton, Palm Beach County, Florida.
- San Clemente City, Orange County, California.
- City of Lancaster, Los Angeles County, California.
- And City of Sterling Heights, Macomb County, Michigan.
For this example, we will address the thickness requirements based on the ACI 332 and based on the cities’ local regulations or standards, just as an example. Based on the ACI 332 the minimum thickness of slabs-on-ground is 3.5 inches.
Boca Raton: Based on Boca Raton’s Driveway Design Affidavit, a residential concrete driveway’s pavement should be 6 inches thick.
San Clemente: Based on San Clemente’s Engineering Division Technical Standards, a residential concrete driveway aisle’s pavement should be at least 6 inches thick.
Lancaster: Based on Lancaster’s Engineering Design Guidelines Policies & Procedures, Section 2.2.10.11.13, and on Section 9 Standard Drawings, a residential concrete driveway should be 4 inches thick.
Sterling Heights: Based on Sterling Heights’s Concrete Guide Permits for Sidewalk & Driveway, driveways should not be less than 4 inches thick.
Other concrete driveway thickness considerations
So far, we explained about the thickness of the pavement for concrete driveways. But there are other thickness considerations that should be taken into account, such as the thickness of the base and the edges.
The base is generally the layer of material that supports the slab. It usually consists of a well graded and compacted granular material. And, similar to pavement requirements, codes, standards, and regulations also state the thickness requirements of the base, which may vary between different locations. But in general, the base thickness should be equal to the thickness of the pavement.
Also, in addition to the base, another thickness consideration lies in the edges. In general, the edges should be thickened about 50%, with 1 in 10 slope, in order to reduce curling.

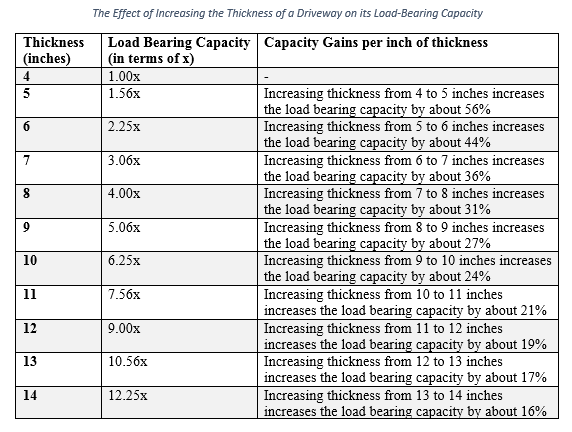
How much will increasing the thickness by an inch increase the load bearing capacity?
In fact, thickness is one of the major factors that influences the load bearing capacity of slabs on ground. The following table summarizes the gains in the load bearing capacity with respect to the increase in thickness.
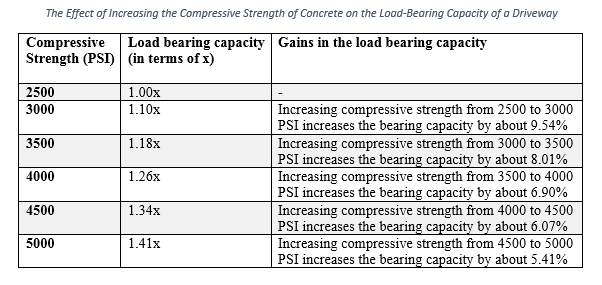
How much will increasing the compressive strength by 500 PSI increase the load bearing capacity?
Basically, the compressive strength of concrete affects the load bearing capacity of slabs on ground, but not as much as thickness does. The following table summarizes the effect of increasing the compressive strength of concrete on the load carrying capacity of a concrete driveway.
Conclusion
It is always important to meet the thickness requirements when designing or constructing concrete driveways. These thickness requirements vary between a location and another, due to differences in the exposure conditions, subgrade properties, and loading conditions. Thereby, it is essential to be aware of the local regulations and codes.
So, in a nutshell, how thick should a concrete driveway be depends on the load, concrete properties, subgrade properties, and the local codes and regulations.
Frequently asked questions
Does adding reinforcement increase the load carrying capacity of my driveway?
Usually, concrete driveways are not structurally reinforced, but the steel is used to serve as shrinkage and temperature reinforcements. Consequently, they do not significantly influence the load bearing capacity of your driveway. Also, they can be used to reduce or even eliminate contraction joints. However, reinforcements can provide flexural strength when concrete cracks.
Bibliography
- (2010). ACI PRC-360-10 Guide to Design of Slabs-on-Ground.
- (2015). ACI 302.1R-15 Guide to Concrete Floor and Slab Construction.
- (2020). ACI 332-20: Code Requirements for Residential Concrete and Commentary.
- Boca Raton Building Department. Driveway Design Affidavit.
- Brisbane City Council. Driveway technical standards.
- (2017). Cement Concrete & Aggregates Australia – Residential Concrete Driveways and Paths.
- City of Lancaster. Section 9 Standard Drawings.
- City of Sterling Heights. (2015). Concrete Guide Permits for Sidewalk & Driveway.
- Lancaster Engineering Division. (1997). Engineering Design Guidelines Policies & Procedures.
- Cringo, B. C., & Anderson, R. B.. Designing Floor Slabs On Grade – Step-by-Step Procedures, Sample Solutions, and Commentary (Vol. Second Edition). (M. K. Hurd, Ed.) 426 South Westgate Addison, , Illinois, United States: The Aberdeen Group.